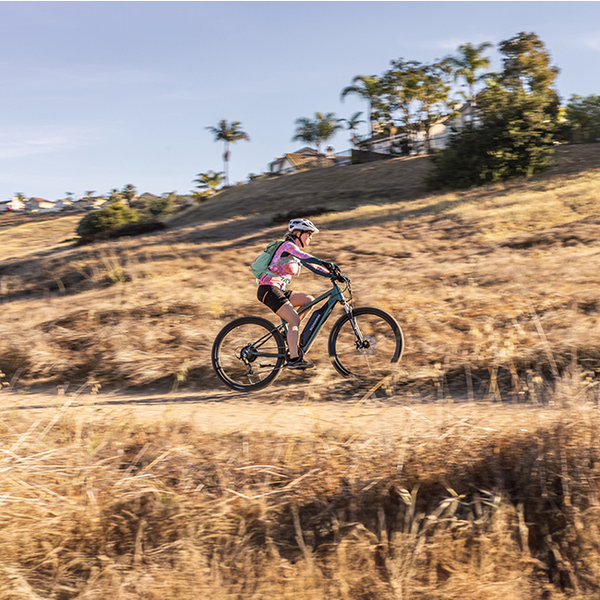
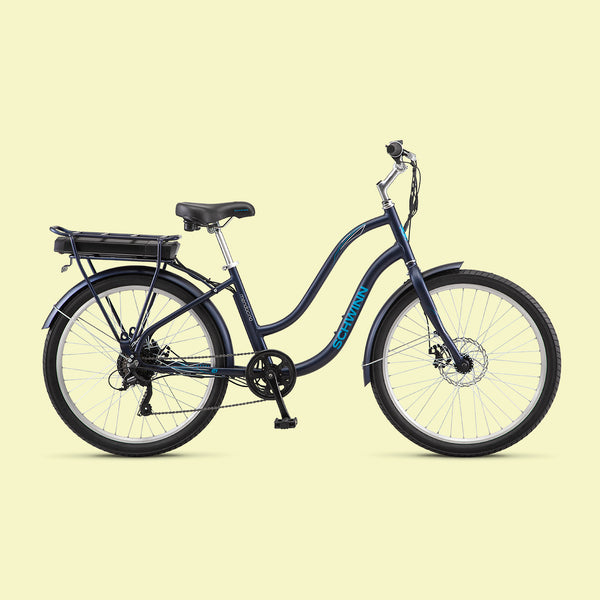
While the first thing that may pop into your mind when you hear electric bicycle is maybe a motor scooter or perhaps even an electric motorcycle, you may be surprised to learn that electric bicycles or e-bikes look almost identical to a regular bicycle – plus a few extras of course!
How Do They Work?
Electric bikes, at their core, are just like any other non-electric or analog bicycle.
While electric bikes and analog bikes have pretty much all the same parts, e-bikes also have an electrical component that gives you an added boost, whenever you need it.
Unlike a motor scooter, the electrical component doesn’t always completely replace the need for pedaling your bicycle. Some bikes have a throttle feature that allows you to rely entirely on the motor to propel the bike, and the main drawback to using the throttle is decreased range.
Regardless of whether you use a throttle or pedal-assist system, an e-bike allows you to travel further and with more ease over obstacles (such as hills) that might have presented a challenge in the past.

Components
Electric bikes have 3 main components that make them different than other normal or analog bicycles. An electric motor, a battery, and a controller. These three components work together to operate the e-bike.
Motor
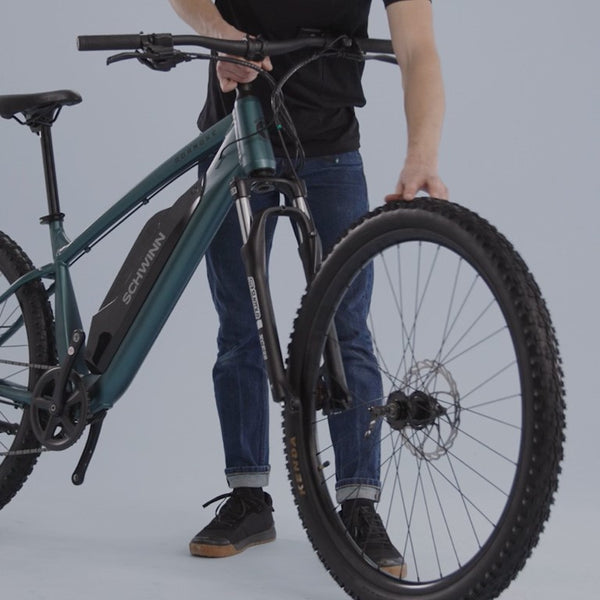
There are several different types of electric motors an e-bike can have. The first type is a front hub motor which is located on the front tire and moves the bicycle forward by spinning the tire, creating a pulling sensation.
There is also a mid-drive motor option that powers the bicycle drivetrain instead of the tire hub. This style creates a natural sensation that one would typically feel when riding a bike.
Finally, as you can see on our new electric bikes, there is also a rear hub motor that is located on the back tire. This type of motor moves the bicycle forward by spinning the back tire.

Controller
The controller can be thought of as the brain of the system. Regardless of the type of motor in the system, the controller takes rider input and communicates it to the battery and motor. It sets the amount of power delivered from the battery to the motor based on the assist level chosen, tells the motor when to turn on/off, and sends information on how the system is working to the system’s display.

Battery
Modern e-bikes use lithium-ion batteries for their electrical stability, storage capacity, longevity, and lighter weight.
E-bike batteries are most commonly rated by Watt-Hours. Common ratings range from 280 watt-hours to 672 watt-hours but can go even higher. To give an idea of the range you can expect from a fully charged battery, you can use a very basic calculation:
If your bike has a 250-watt motor with a 360-watt hour battery, at the highest assist level you would get up to 45 miles of use from the bike before needing to charge the battery again. There are several variables that can increase or decrease that range (wind and terrain conditions, how much pedal power you supply, the assist level you choose, carrying extra weight on the bike, etc.).

Charging
Charging your bicycle is easy! Most e-bikes allow for charging on or off the bike. There is a charge port built into the frame to allow you to charge the bike with the battery installed, or if more convenient, you can unlock the battery from the bike and take it into your home or office to charge separately.

Styles
Just like regular bikes, e-bikes are available in a variety of styles, including cruiser, hybrid, and mountain. Each style is tailored to a particular terrain and type of ride. That means you’ll want to consider how and where you ride when choosing an e-bike. Here’s the breakdown:
- Cruiser: Ideal for casual rides on pavement; features a relaxed upright riding position and wide comfort tires.
- Hybrid: Best for commuting and recreation on pavement and light trails; features an upright riding position with medium-width, multi-use tires.
- Mountain: Great for riding rugged trails or around the neighborhood; features a forward riding position and wide knobby tires.

So, what are you waiting for? It’s time to do more with an e-bike! Check out our electric bikes, and let’s go!